Blockchain technology is an amazing invention that has revolutionized asset tracking, transaction processing, and trust-building. Allow me to explain it to you:
How Does Blockchain Work?
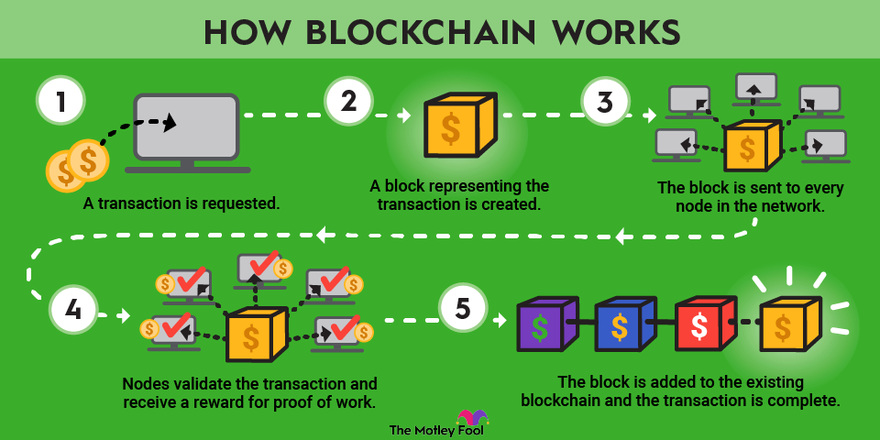
A distributed ledger known as a blockchain is made up of expanding lists of entries, or blocks, that are safely connected by cryptographic hashes. Each block has transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the block before it. Each block links to the ones before it, forming an effective chain as each block includes information about the one before it.
Transactions on the Blockchain Network.
As a result, once a blockchain transaction is recorded, it cannot be undone in the past without also changing all blocks that follow it. This makes blockchain transactions irreversible.
On a blockchain network, almost anything valuable can be recorded and exchanged, lowering costs and risk for all parties.
Information is the foundation of business, and blockchain technology is perfect for distributing it. It offers real-time, shareable, and visible data that is kept on an unchangeable ledger that is only accessible by network users with permission.
A blockchain network can monitor accounts, production, payments, orders, and much more. Members benefit from increased efficiency, self-assurance, and access to new prospects since they hold a single perspective of reality.
Principal components of a blockchain
- Distributed Ledger: The distributed ledger, which keeps an unchangeable record of all transactions, is accessible to any member of the network. Duplication of effort is avoided because transactions are only recorded once.
- Immutability: No party may alter or tamper with a transaction after it has been recorded. When something goes wrong, you have to add a new transaction to fix it, and both transactions stay accessible.
- Smart Contracts: These are collections of automatically executed rules that are kept on the blockchain. They provide the prerequisites for several activities, like the payment of travel insurance or the transfer of company bonds.
- Data Blocks: Every block contains details regarding the movement of an asset, including who, what, when, where, and how much. It may even cover things like a food shipment's temperature.
- Chained Blocks: Data is organized into a chain when blocks are transferred or ownership is changed. The blocks, which are safely connected to one another to prevent tampering, validate the precise timing and order of transactions.
- Tamper-Evident: The immutability of blockchain eliminates the potential for hostile actors to tamper with the ledger, creating a reliable record.
Blockchain's advantages
- Efficiency: Get rid of redundant documentation and third-party verifications.
- Transparency: Offers a public, transparent ledger system.
- Security: Guarantees documents are tamper-evident.
- Trust: Fosters a sense of trust among network users.
Use Cases for Blockchain
- Blockchain is used by cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, Bitcoin, and others to facilitate safe transactions.
- Supply Chain Management: Track goods from manufacturer to retailer while preventing fakes.
- Healthcare: Protect patient privacy while securely exchanging patient records between hospitals.
- Real estate: Decrease fraud and streamline property transfers.
What Does Blockchain Decentralization Mean?
Decentralization is one of the key ideas in blockchain technology. The chain cannot be owned by one computer or one business. Rather, it functions as a distributed ledger across the chain's nodes. Any type of electronic device that saves copies of the chain and keeps the network running can be a blockchain node.
Each node has a copy of the blockchain, and for the chain to be updated, trusted, and validated, the network must algorithmically approve each newly mined block. Blockchains have built-in security since every transaction in the ledger can be readily verified and inspected. A distinct alphanumeric identification number that displays each participant's transactions is provided.
By integrating open data with a check-and-balance mechanism, the blockchain can preserve its integrity and foster user confidence. In essence, blockchains are just the technological scalability of trust.
A Blockchain Platform: What Is It?
The term blockchain platform describes a platform via which users can engage with a blockchain and its network, whereas a blockchain network specifies the infrastructure of a distributed ledger. Blockchain platforms are designed to be scalable and function as add-ons to an already-existing blockchain infrastructure, enabling services and information sharing to be enabled by this framework directly.
Ethereum is a software platform that runs the Ethereum cryptocurrency, often known as ether. It is an example of a blockchain platform. Users of the Ethereum platform can also develop smart contracts and programmable tokens, which are based directly on the Ethereum blockchain.

great
ReplyDeletePost a Comment